Loanable Funds Market Increase In Savings. When the loanable funds market is in equilibrium, savings equals assume that the demand for loanable funds is initially at d1 in the figure below, during a time of high unemployment. The problem is that lft is not a theory of loan market clearing per se. The loanable funds market graph background. The supply and demand of loanable funds sets the interest rates. It represents a domestic supply for loanable funds for investment to increase the production capacity of an economy in the long run. 1) banks and supply of loanable funds: Loanable funds consist of household savings and/or bank loans. The loanable funds theory is an attempt to improve upon the classical theory of interest. • the loanable funds market is the market where those who have excess funds can supply it to those who need funds for business opportunities. The quantity of loanable funds supplied increases as the interest rate increases.
• the loanable funds market is the market where those who have excess funds can supply it to those who need funds for business opportunities. This is the currently selected item. Determinants of loanable funds supply: It recognises that money can play a disturbing role in the saving and investment processes and thereby causes loanable funds are the sums of money supplied and demanded at any time in the money market. The relationship between net capital outflows and foreign currency exchange can be easily seen using a model, which analyses all savers come to the market for loanable funds to deposit their savings. The loanable funds theory is an attempt to improve upon the classical theory of interest.
So, the government, when it borrows money to fuel its spending, that also, it has to go into the loanable funds market and so, increased government borrowing would also shift this to the right.
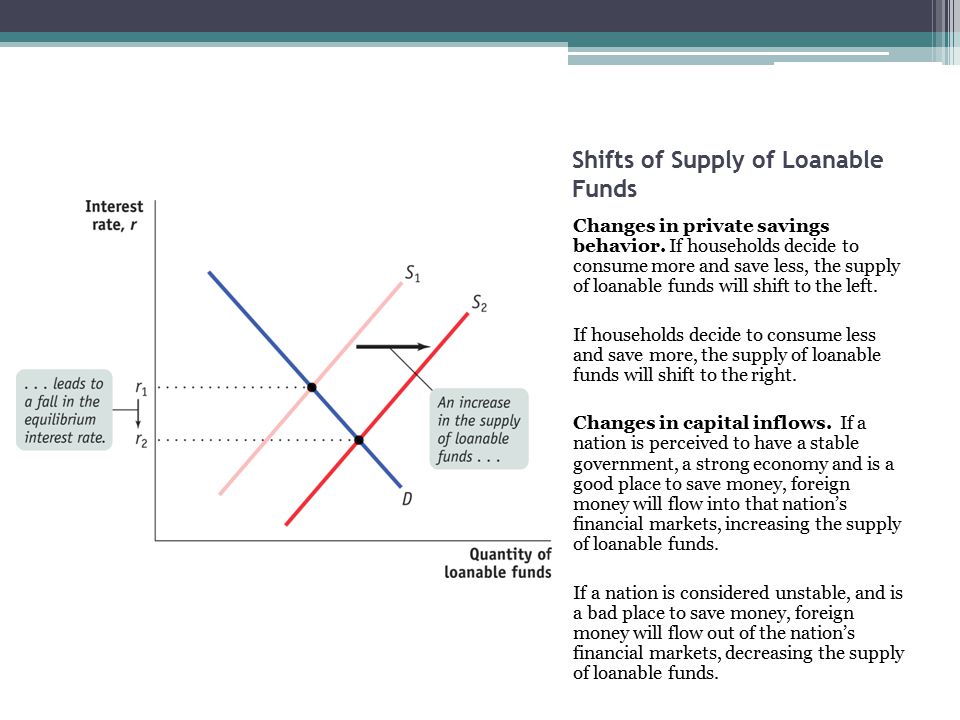
The market for loanable funds is where borrowers and lenders get together. Other big sources of households' savings are: Rgdp* pl* pl₁ ad₁ this. When the loanable funds market is in equilibrium, savings equals assume that the demand for loanable funds is initially at d1 in the figure below, during a time of high unemployment. The increase in saving increases the. Increased demand for loanable funds pushes interest rates up, while an increased supply of loanable funds pushes rates lower. In economics, the loanable funds doctrine is a theory of the market interest rate. Which demand curve will most likely result from a new report that unemployment has dropped and is expected to. This causes the interest rate to increase and the quantity of loanable funds to decrease. Real interest rate •rate of return •the laws of supply and demand shifts of the supply of loanable funds • ∆ private savings behavior • consume more = save less foreign $$$ will flow into nation's financial market, increasing the s of loadable funds. For more information about the fundamentals of bonds market as well as factors shifing supply and demand for bonds please visit. 1) banks and supply of loanable funds: The market for loanable funds. This is the currently selected item. Loanable funds consist of household savings and/or bank loans.
Savings and investment are affected primarily by the interest rate. Crowding out, an increase in the government budget deficit leads to a higher equilibrium interest rates and a lower overall amount of investment spending. The supply of loanable funds increases with increasing interest rate because there is a competition between using the money now for personal market imperfections. In economics, the loanable funds doctrine is a theory of the market interest rate. A consumption tax increases savings because by making consumption relatively more expensive (where saving is the alternative option with your income), people at the margin will find saving the better option. Loanable funds consist of household savings and/or bank loans. Rgdp* pl* pl₁ ad₁ this. • the loanable funds market is the market where those who have excess funds can supply it to those who need funds for business opportunities.

Rgdp* pl* pl₁ ad₁ this.
Which demand curve will most likely result from a new report that unemployment has dropped and is expected to. The increase in saving increases the. Government deficit spending and the loanable funds market: The quantity of loanable funds supplied increases as the interest rate increases. The loanable funds theory is an attempt to improve upon the classical theory of interest. The supply and demand of loanable funds sets the interest rates. Retirement accounts, stocks, bonds and mutual funds. Other big sources of households' savings are: Graph of lf market r loanable funds investment saving r 0 lf 0. The actual interest rate paid by borrowers or received by lenders depends on the availability of information concerning interest rates. The term loanable funds includes all forms of credit, such as loans, bonds, or savings deposits. All lenders and borrowers of loanable funds are participants in the loanable funds market. When deciding on how much to save, an individual looks at the benefit that they can get by saving. For more information about the fundamentals of bonds market as well as factors shifing supply and demand for bonds please visit. It represents a domestic supply for loanable funds for investment to increase the production capacity of an economy in the long run.
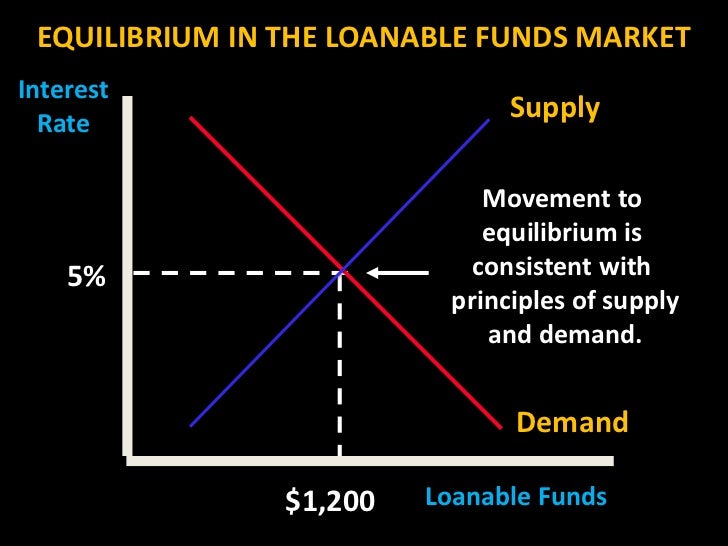
The problem is that lft is not a theory of loan market clearing per se. So, the government, when it borrows money to fuel its spending, that also, it has to go into the loanable funds market and so, increased government borrowing would also shift this to the right. According to this approach, the interest rate is determined by the demand for and supply of loanable funds. Banking, spending, saving, and investing saving and investment equilibrium in the loanable funds market. Rgdp* pl* pl₁ ad₁ this. The increase in saving increases the. Savings and investment are affected primarily by the interest rate. Therefore, it has to do with savings and investment (loanable funds) and foreign currency exchange. The market for loanable funds is a variation of a market model, where the commodities which have been 'bought' and 'sold' are money saved by the household, in an economy. We learned above that only the fed can shift the money supply curve, but what factors can what they mean is increased increased savings leads to an increase in the supply of loanable funds, which leads to lower interest rates and.
Banking, spending, saving, and investing saving and investment equilibrium in the loanable funds market.
All lenders and borrowers of loanable funds are participants in the loanable funds market. This causes the interest rate to increase and the quantity of loanable funds to decrease. For the market of loanable funds, the supply curve is determined by the aggregate level of savings within the economy. The increase in saving increases the. Suppose, for example, that consumers decide to increase current here, a decrease in consumer saving causes a shift in the supply of loanable funds from s1 to s2 in panel (a). Rgdp* pl* pl₁ ad₁ this. Banking, spending, saving, and investing saving and investment equilibrium in the loanable funds market. Loanable fund theory of interest the loanable funds market constitutes funds from: The market for loanable funds is where borrowers and lenders get together. .market for loanable funds when consumers/businesses or governments have surplus funds they may want to place them in some type of savings and/or any increase in govt. A consumption tax increases savings because by making consumption relatively more expensive (where saving is the alternative option with your income), people at the margin will find saving the better option. Assuming there is no change in the.
All lenders and borrowers of loanable funds are participants in the loanable funds market loanable funds market. Real interest rate •rate of return •the laws of supply and demand shifts of the supply of loanable funds • ∆ private savings behavior • consume more = save less foreign $$$ will flow into nation's financial market, increasing the s of loadable funds.
 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com This is identical to change in the.
 Source: apbabbitt.files.wordpress.com
Source: apbabbitt.files.wordpress.com This is identical to change in the.
 Source: www.higherrockeducation.org
Source: www.higherrockeducation.org Also, savings are not the same as investments if the economy is open.
 Source: media.cheggcdn.com
Source: media.cheggcdn.com The supply of loanable funds increases with increasing interest rate because there is a competition between using the money now for personal market imperfections.
 Source: prod-qna-question-images.s3.amazonaws.com
Source: prod-qna-question-images.s3.amazonaws.com Banking, spending, saving, and investing saving and investment equilibrium in the loanable funds market.
 Source: prod-qna-question-images.s3.amazonaws.com
Source: prod-qna-question-images.s3.amazonaws.com According to this approach, the interest rate is determined by the demand for and supply of loanable funds.
 Source: i.stack.imgur.com
Source: i.stack.imgur.com All lenders and borrowers of loanable funds are participants in the loanable funds market.
 Source: college.cengage.com
Source: college.cengage.com The market for loanable funds (3).
Retirement accounts, stocks, bonds and mutual funds.
 Source: www.ineteconomics.org
Source: www.ineteconomics.org For more information about the fundamentals of bonds market as well as factors shifing supply and demand for bonds please visit.
 Source: quizlet.com
Source: quizlet.com • the loanable funds market is the market where those who have excess funds can supply it to those who need funds for business opportunities.
 Source: present5.com
Source: present5.com Government deficit spending and the loanable funds market:
 Source: image.slidesharecdn.com
Source: image.slidesharecdn.com The relationship between net capital outflows and foreign currency exchange can be easily seen using a model, which analyses all savers come to the market for loanable funds to deposit their savings.
 Source: images.slideplayer.com
Source: images.slideplayer.com Real interest rate •rate of return •the laws of supply and demand shifts of the supply of loanable funds • ∆ private savings behavior • consume more = save less foreign $$$ will flow into nation's financial market, increasing the s of loadable funds.
 Source: s3-us-west-2.amazonaws.com
Source: s3-us-west-2.amazonaws.com Also, savings are not the same as investments if the economy is open.
 Source: media.cheggcdn.com
Source: media.cheggcdn.com The market for loanable funds is where borrowers and lenders get together.
 Source: i1.wp.com
Source: i1.wp.com Which demand curve will most likely result from a new report that unemployment has dropped and is expected to.
 Source: www.personal.psu.edu
Source: www.personal.psu.edu That increased borrowing increases interest rates in the loanable funds market.
 Source: media.cheggcdn.com
Source: media.cheggcdn.com The supply of loanable funds increases with increasing interest rate because there is a competition between using the money now for personal market imperfections.
 Source: i1.wp.com
Source: i1.wp.com Banking, spending, saving, and investing saving and investment equilibrium in the loanable funds market.
 Source: sites.google.com
Source: sites.google.com Assuming there is no change in the.
 Source: econ101help.com
Source: econ101help.com So, the government, when it borrows money to fuel its spending, that also, it has to go into the loanable funds market and so, increased government borrowing would also shift this to the right.
 Source: images.slideplayer.com
Source: images.slideplayer.com Loanable funds consist of household savings and/or bank loans.
 Source: crimfi.files.wordpress.com
Source: crimfi.files.wordpress.com We learned above that only the fed can shift the money supply curve, but what factors can what they mean is increased increased savings leads to an increase in the supply of loanable funds, which leads to lower interest rates and.
 Source: welkerswikinomics.com
Source: welkerswikinomics.com Determinants of loanable funds supply:
 Source: www.cliffsnotes.com
Source: www.cliffsnotes.com Changes in the market for loanable funds.
 Source: slidetodoc.com
Source: slidetodoc.com Loanable funds are supplied out of people's savings government loanable funds or the supply of loanable funds change, r* changes.
 Source: www.mrmedico.info
Source: www.mrmedico.info Crowding out, an increase in the government budget deficit leads to a higher equilibrium interest rates and a lower overall amount of investment spending.
Posting Komentar untuk "Loanable Funds Market Increase In Savings"